DevOps
DevOps
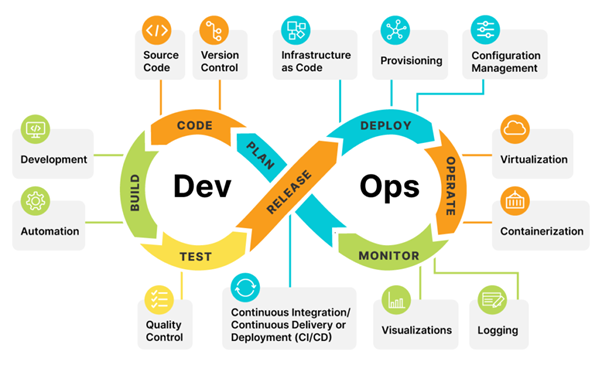
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools
that increases an organization's ability to deliver applications and services
at high velocity: evolving and
improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional
software development and infrastructure management processes.
DevOps focuses on breaking down traditional silos between development
and operations, enabling a more seamless and iterative approach to software
development. Some key principles and practices of DevOps include:
Continuous Integration (CI): Developers frequently integrate their code changes into a shared repository. Automated tests and code analysis are executed to catch integration issues early.
Continuous Delivery (CD): Automated deployment
pipelines ensure that code changes are tested, validated, and ready for
production deployment at any point in time. This includes automated testing,
building, and packaging of software.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Infrastructure is defined
and managed through code, allowing for consistent and repeatable provisioning
and configuration of resources. Tools like Terraform and Ansible are commonly
used for this purpose.
Automated Testing: Automated testing practices, such as unit
tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests, are integral to DevOps. They
help identify bugs and regressions early in the development cycle.
Automated Tools For Devops :
Monitoring
and Logging: Continuous monitoring of applications and infrastructure
helps identify performance bottlenecks, errors, and other issues in real-time.
Logging provides valuable insights for troubleshooting and optimizing systems.
Collaboration
and Communication: DevOps emphasizes open communication and collaboration
between development, operations, and other relevant teams. This can lead to
quicker problem-solving and knowledge sharing.
Version Control: Version control systems like Git are crucial
for tracking changes to code and coordinating collaboration among developers.
Microservices and Containerization: These approaches allow
breaking down applications into smaller, independently deployable components,
making it easier to manage, scale, and update them.
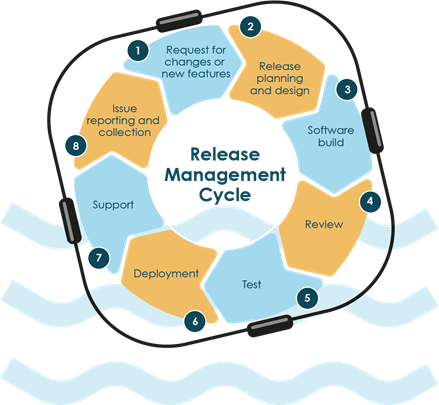
Release Management: DevOps practices enable frequent and
incremental releases, reducing the risk associated with large, infrequent
releases.
By
V Tamilmani
21UCA049










Comments
Post a Comment